Pushing the Boundaries of Innovation – METS Ignited Tranche 4 Collaborative Project Update
New waves of technology and innovation continue to disrupt industry across the globe. Advancements in automation, artificial intelligence and machine learning provide significant opportunities for miners.
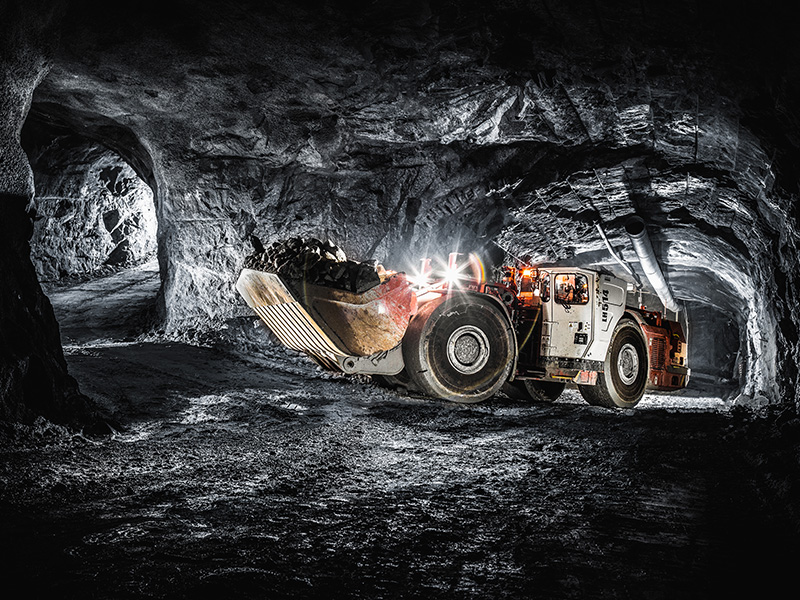
Polymathian has been applying ground-breaking technology through a METS Ignited Industry Growth Centre Collaborative Project. The $2 million industry-led collaborative project leveraging government funding was awarded to Polymathian to deploy ORB, its mine optimisation software, at OZ Minerals’ underground Carrapateena mine in South Australia.
Representing industry's continued investment in innovation, ORB is the world's first and most advanced Short Interval Control system for near real-time optimisation of mine planning and scheduling activities.
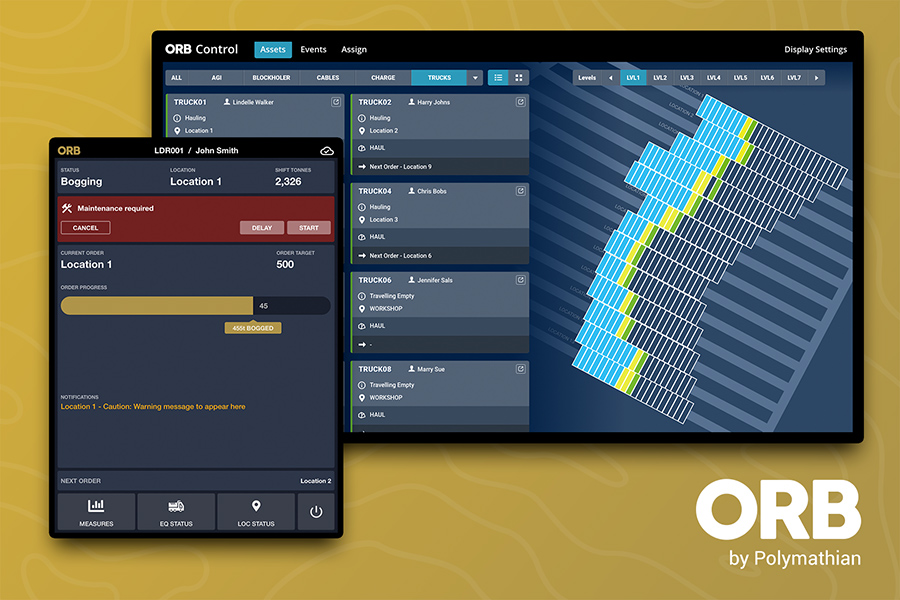
ORB is currently being used for block cave mining in Australia and around the world, where it has demonstrated an improvement to mining productivity. Industry investment has enabled Polymathian to expand ORB's capabilities to include other underground mining methods and accelerate its growth domestically and internationally. As a result, Polymathian and its project partners have created additional jobs and new career pathways for industry to meet the project's demands.
“Project investment has allowed us to add additional software developers and business development staff, increasing our headcount by approximately 10% in our Brisbane and Perth offices. It has also enabled us to gain additional traction with existing clients and attract new interest globally,” said Polymathain co-founder and ORB product leader Steven Donaldson.
The first phase of the project is to plan the dispatch of equipment at the start of a shift using ORB optimisation software. In partnership with OZ Minerals, Polymathian has been able to harness practical knowledge of operational staff to produce better solutions, have more automated inputs and be more user friendly.
The step-change ORB represents in mining innovation lies in producing underground mine development and production plans autonomously that are consistently optimised using industrial mathematics. Removing the iterative and complex process of manual mine planning provides many benefits; including smarter decision making and more agile mine operations capable of responding to real-time conditions.
Mine planning plays an often misunderstood but nonetheless essential role in the achievement of high performance. Related: The role of mine planning in high performance
"One of the great value propositions for the ORB software is to free the Shift Supervisor from the arduous task of equipment scheduling and dispatch, and allow them to truly focus on leading their team of underground miners", said Project Manager and OZ Minerals Mining Superintendent Daniel Bruce.
Ensuring safety is a key responsibility for mining supervisors. With the introduction of automation, mine planning can be made more efficient. Instead of spending hours a day working on a complex spreadsheet to plan the shift, shift supervisors can spend that valuable time with their team, and to focus more on making strategic decisions.
This collaborative project is enhancing ORB to produce optimised strategic mine plans that interface with the short interval control system to influence key priorities. ORB then autonomously dispatches tasks to equipment operators in near real-time to ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
As mining gets deeper and more complex, efficiency gains introduced by using tools such as ORB can help overcome cumbersome manual decision-making processes found in more conventional mining practices.
Incorporating numerous advances in digital twin technologies with real-time data feeds, automated and optimised mine planning, and just-in-time dispatch to equipment operators, these advances improve mine productivity and maximise profitability by prioritising the right work at the right locations.
Upon completion of this project, OZ Minerals’ Carrapateena Mine will be the world's first sub-level cave mine to utilise highly automated Short Interval Control backed by Industrial Mathematics to manage operations.
Originally published by the AusIMM Bulletin






